Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sakai, Kenji; Oku, Takayuki; Okudaira, Takuya; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Hirota, Katsuya*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011116_1 - 011116_6, 2021/03
In neutron fundamental physics, study of correlation term  of a neutron spin
of a neutron spin 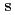 and a target nuclear spin
and a target nuclear spin 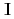 is important because
is important because  term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to
term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to 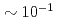 by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study
by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study  term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by
term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by  term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of
term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of  Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change
Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change  of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (
of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (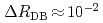 ) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of
) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of  has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained
has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained  in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
Li, H.; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Tanimura, Naoki*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 27(24), p.246001_1 - 246001_5, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:27.97(Physics, Condensed Matter) and its homologues
and its homologuesAnton, J.*; Hirata, Masaru; Fricke, B.*; Pershina, V.*
Chemical Physics Letters, 380(1-2), p.95 - 98, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:18.14(Chemistry, Physical)We use the newly developed non collinear spin polarized density functional method to describe the tetrachlorides of element Rutherfordium (Rf) and its homologues. It is the first time that a real three-dimensional molecule is described with this method. Without any additional corrections (used so far for the atomic values) we get nearly complete agreement for all homologues and thus a good prediction for the unknown value for RfCl .
.
Takeda, Masayasu; Torikai, Naoya*; Ino, Takashi*; Tasaki, Seiji*
KENS Report-XIV, p.205 - 206, 2003/00
no abstracts in English
 He neutron spin filters at J-PARC MLF
He neutron spin filters at J-PARC MLFOku, Takayuki
no journal, ,
We have been developing a  He neutron spin filter (NSF) for the efficient utilization of pulsed neutrons, since the
He neutron spin filter (NSF) for the efficient utilization of pulsed neutrons, since the  He NSF is effective for neutrons in the wide energy range. The
He NSF is effective for neutrons in the wide energy range. The  He NSF is effective especially for neutrons with energy higher than several-tens-meV. It also can cover a large solid angle and polarize neutrons without deflecting them from their original trajectory, it is suitable for the analyzer for SANS and reflectometer instruments. In addition, the
He NSF is effective especially for neutrons with energy higher than several-tens-meV. It also can cover a large solid angle and polarize neutrons without deflecting them from their original trajectory, it is suitable for the analyzer for SANS and reflectometer instruments. In addition, the  He NSF will be a key device in the application of recently developed magnetic field imaging technique by using polarized pulsed neutrons, since it can polarize a thick neutron beam without deteriorating projection image of the transmitted neutrons. In order to apply the
He NSF will be a key device in the application of recently developed magnetic field imaging technique by using polarized pulsed neutrons, since it can polarize a thick neutron beam without deteriorating projection image of the transmitted neutrons. In order to apply the  He NSF to experiments at a pulsed neutron experimental facility such as the J-PARC, it is important to make the system stable and easy to setup and operate, because the system is located inside thick and bulky radiation shields for high energy gamma ray and neutrons. In this talk, we will report the development and application status of the
He NSF to experiments at a pulsed neutron experimental facility such as the J-PARC, it is important to make the system stable and easy to setup and operate, because the system is located inside thick and bulky radiation shields for high energy gamma ray and neutrons. In this talk, we will report the development and application status of the  He NSF at J-PARC MLF.
He NSF at J-PARC MLF.